Penghai Zhao, Qinghua Xing, Kairan Dou, Jinyu Tian, Ying Tai, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xiang Li
arXiv pre-print
2024y Aug
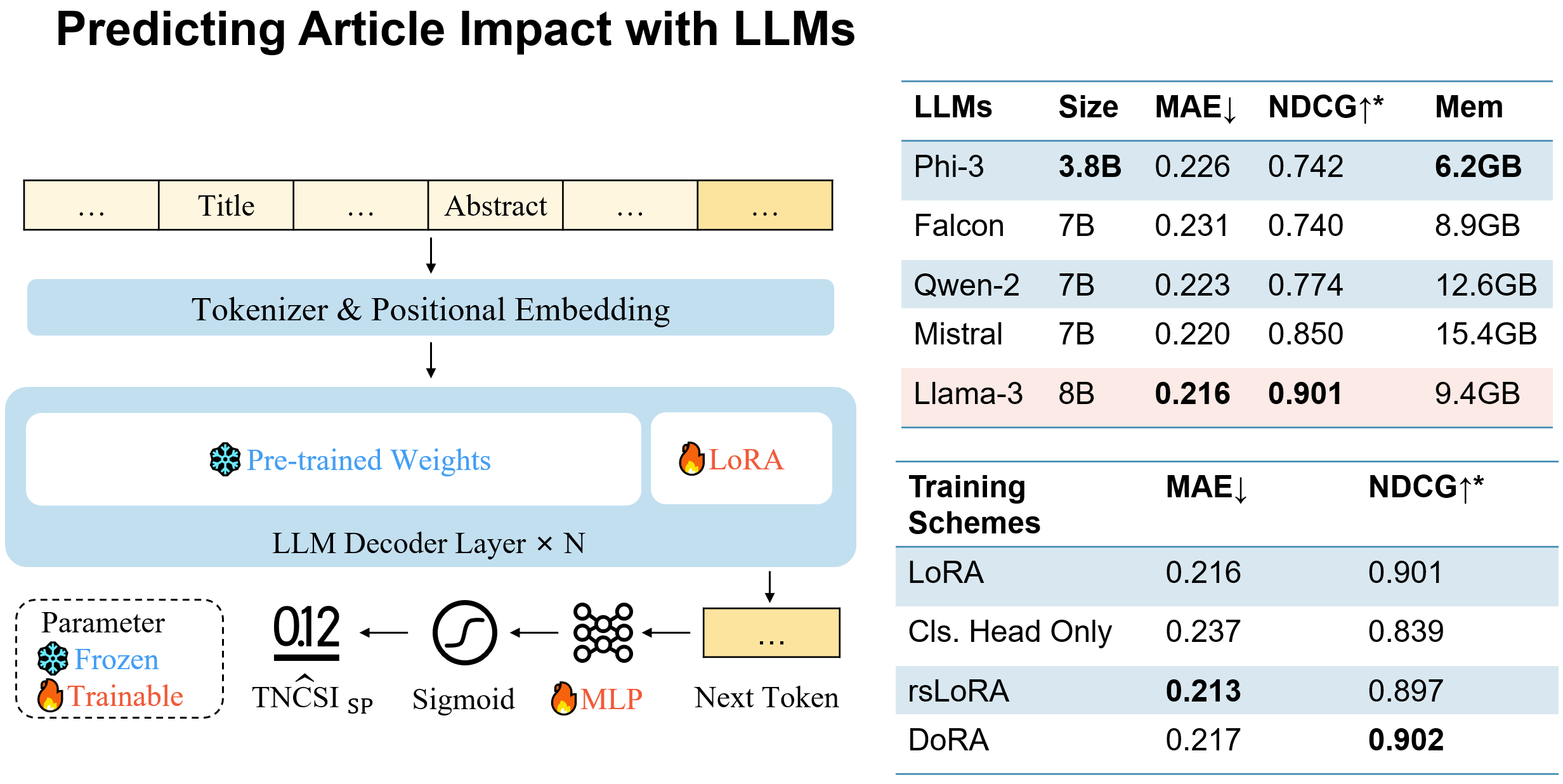
As the academic landscape expands, the challenge of efficiently identifying potentially high-impact articles among the vast number of newly published works becomes critical. This paper introduces a promising approach, leveraging the capabilities of fine-tuned LLMs to predict the future impact of newborn articles solely based on titles and abstracts. Moving beyond traditional methods heavily reliant on external information, the proposed method discerns the shared semantic features of highly impactful papers from a large collection of title-abstract and potential impact pairs. These semantic features are further utilized to regress an improved metric, TNCSI_SP, which has been endowed with value, field, and time normalization properties. Additionally, a comprehensive dataset has been constructed and released for fine-tuning the LLM, containing over 12,000 entries with corresponding titles, abstracts, and TNCSI_SP. The quantitative results, with an NDCG@20 of 0.901, demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting the impact of newborn articles when compared to competitive counterparts. Finally, we demonstrate a real-world application for predicting the impact of newborn journal articles to demonstrate its noteworthy practical value. Overall, our findings challenge existing paradigms and propose a shift towards a more content-focused prediction of academic impact, offering new insights for assessing newborn article impact.
Penghai Zhao, Xin Zhang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Jian Yang, Xiang Li
arXiv pre-print
2024y Feb
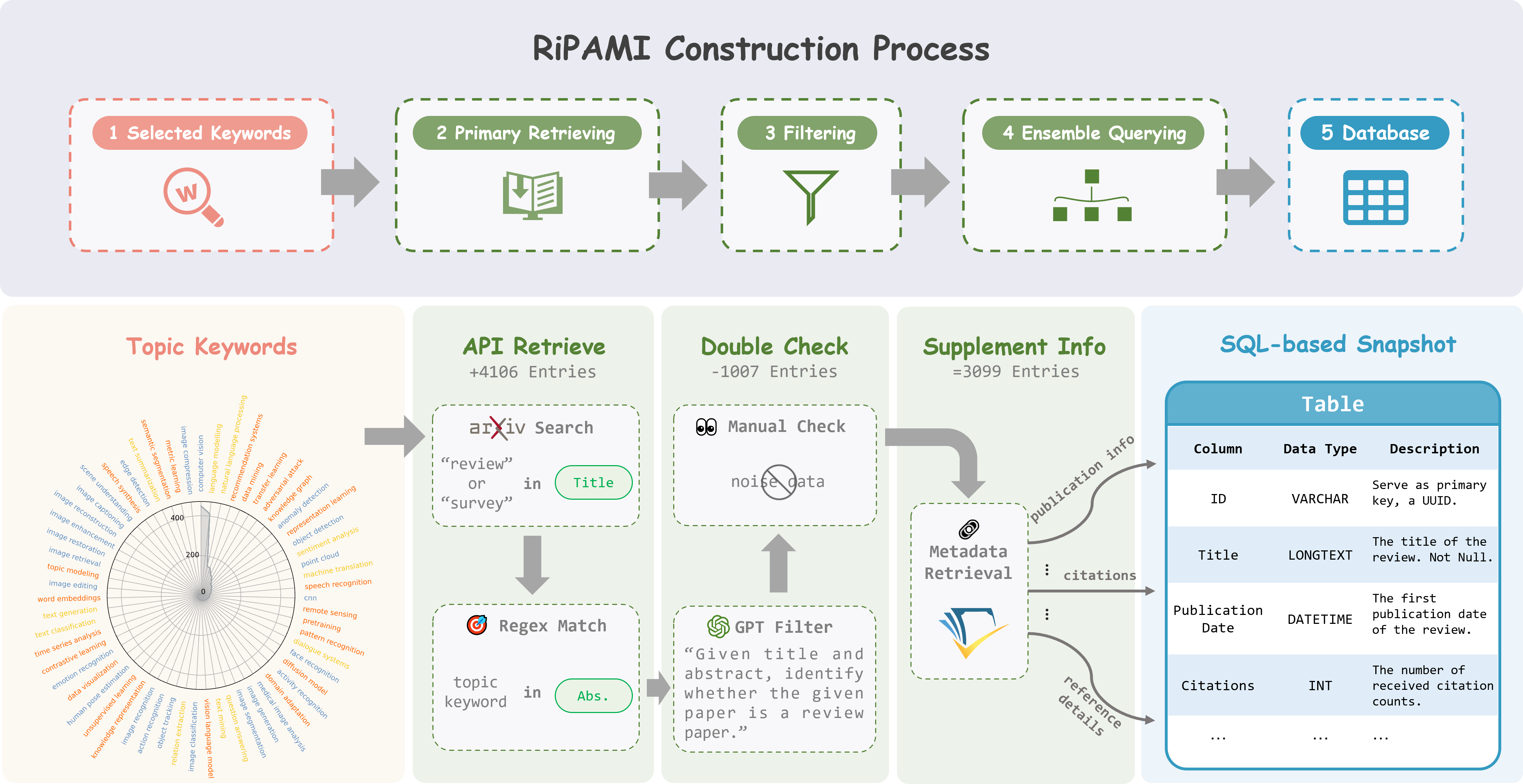
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence and computational methods have propelled significant progress in the Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI) field, spawning a proliferation of diverse knowledge. Within this rapidly expanding body of knowledge, literature reviews play a crucial role in synthesizing fragmented information, offering researchers a comprehensive understanding of the investigated topic and thus earning widespread recognition for their value. In this study, we examine and synthesize literature reviews within the PAMI field. Beginning with a narrative overview, we highlight common preferences adopted by authors when composing PAMI reviews. Following this, we provide a statistical analysis of these preferences and other data on the RiPAMI , a database containing over 3,000 reviews. Furthermore, we introduce a set of bibliometric indicators designed to assess several key aspects, such as the impact of literature reviews and the quality of their references. Statistical bibliometrics analysis of the RiPAMI reveals a positive correlation between the reference quality and academic impact. Meanwhile, an analysis of AI-generated review samples uncovers a critical limitation: their difficulty in evaluating the academic value of newly published articles undermines their ability to identify cutting-edge research compared to human-authored reviews. Finally, we discuss how the proposed bibliometrics indicators can assist researchers in managing the growing volume of literature reviews and offering valuable insights into current challenges and future directions for literature reviews in PAMI.
2022y May

As a common font of Tibetan, Uchen is widely used in various kinds of Tibetan document at different times. In recent
years, ongoing digitalization imposes increasing demands on automated optical character recognition which makes Uchen
document layout analysis and recognition system much more meaningful and useful. Extensive research has shown that
traditional methods have the capacity to extract text from contemporary documents. However, accurate binarization,
layout analysis, and recognition still remain real challenges, especially when facing the Kangyur, a kind of historical
Tibetan document featuring non-uniform illumination, mottled background and considerable touching components. In this
thesis, traditional and deep learning-based studies have been conducted on both contemporary and historical Tibetan
documents. Major contributions are as follows:
(1) Printed Tibetan document analysis and recognition. Traditional binarization methods were adopted to generate the
binarization results for the printed Tibetan document images. Based on the resulted binary images, the present work
employed techniques including the Hough transform and connected components analysis to extract layout information from
the document images. In addition, CNN was adopted to classify the printed Tibetan character. The proposed CNN achieves
the recognition accuracy of 99.77% while being low-complexity.
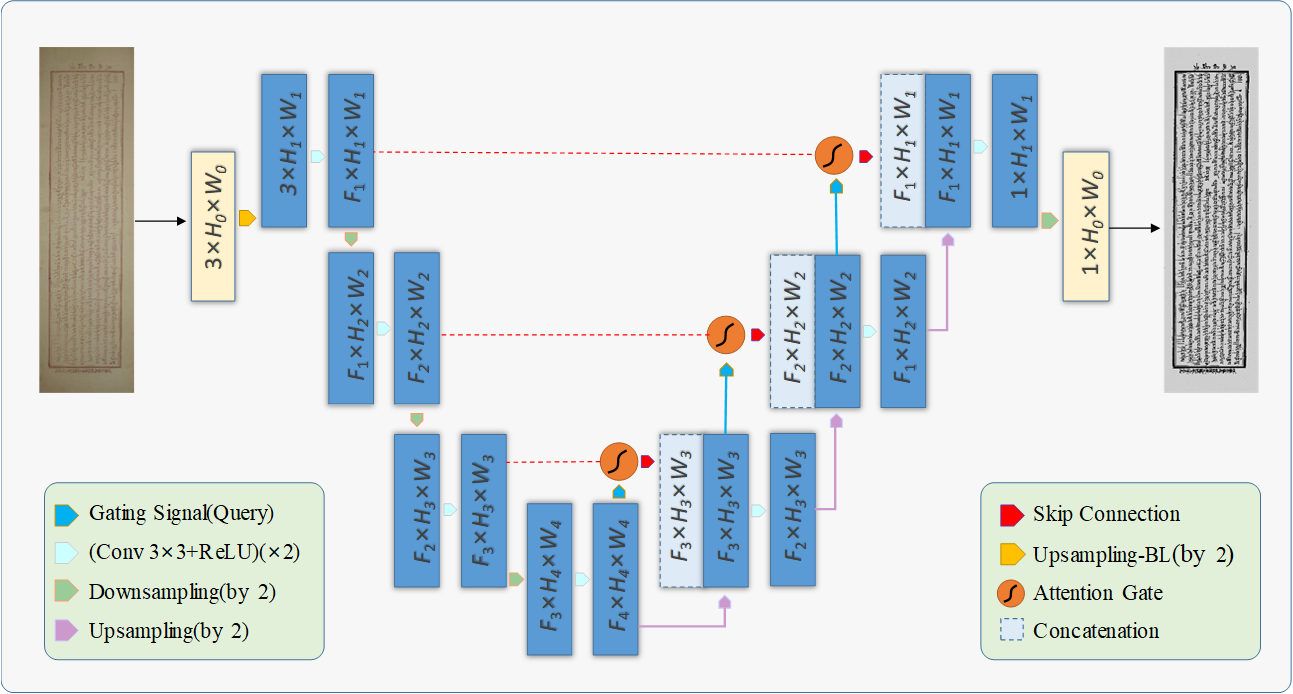
(2) Historical Tibetan document analysis and recognition. This thesis proposes upsampling the input with corresponding
downsampling of the output as an easy-to-use solution for U-Net based approaches which is effective on our dataset and
the DIBCO 2017 dataset. The quantitative experimental results shows that the proposed method can alleviate the
pseudo-touching and achieves an average P-FM of 97.73 which is two percentage points higher than the result of U-Net. To
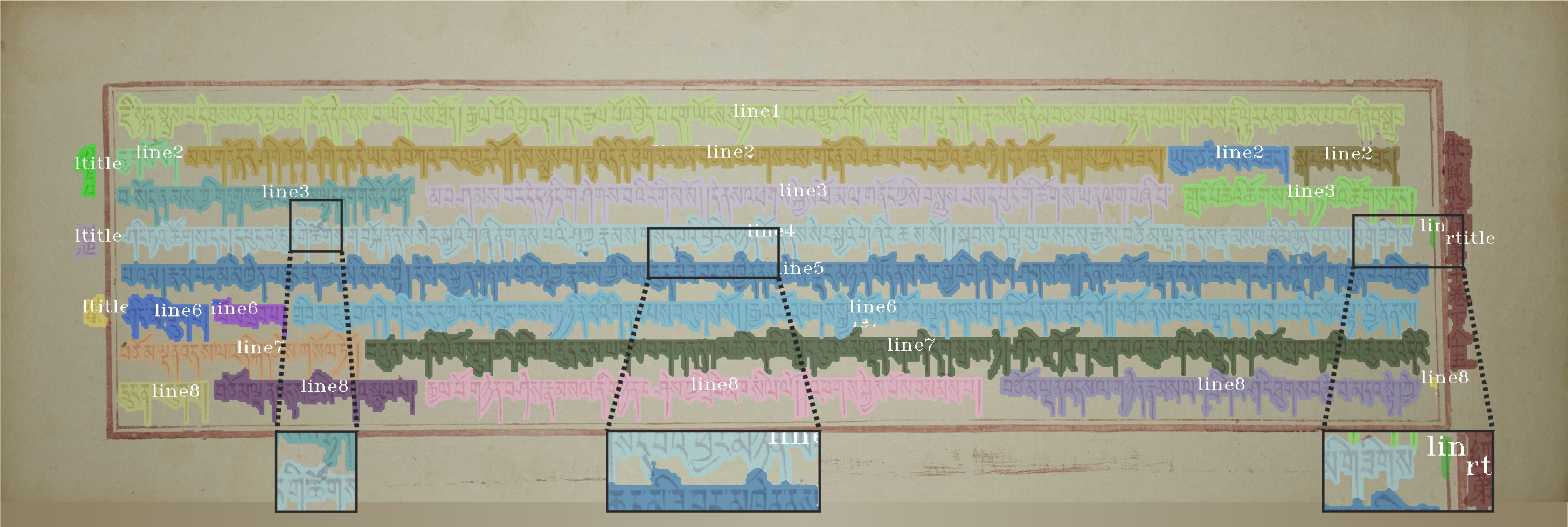
obtain superior prediction at text image boundaries, a sub-line level layout analysis approach based on the SOLOv2 is
presented. The experimental results show that the proposed method delivers a decent 72.7% AP on our dataset that
suggests anchor-free networks’ advantage in layout analysis. This thesis also proposes an end-to-end recognition network
christened TSViT and develops the overlapping recognition strategy. TSViT achieves 84.47% accuracy on the test set.
(3) The Design and Realization of the Uchen Document Layout Analysis and Recognition System. Following the modular
design philosophy of ‘high coheres, low coupling’, this thesis uses PyQT5, OpenCV, and Pytorch to complete the
development of the stable and flexible system. The binarization, layout analysis, and recognition functions can perform
well during the software tests which satisfy the practical requirements.
See more at 《乌金体藏文文档版面分析与识别系统》
P Zhao, W Wang, G Zhang, Y Lu
Neural Computing and Applications
2021y Oct
Binarization, one of the most popular research directions in computer vision, is still facing challenges, especially for the degraded historical Tibetan document images. Quite a few U-Net-based binarization approaches might encounter a particular problem called pseudo-touching which hampers subsequent procedures including text line segmentation, character segmentation, and recognition. To avoid these undesired pseudo-touching strokes and obtain optimal binary images, the present work employs several easy-to-use techniques, such as rescaling the input and output of the attention U-Net. Furthermore, we provide insights into the accelerated construction of the training set and discuss the effects of various configurations. The quantitative experimental results on our dataset show that upsampling the input image by a factor of two during the inference phase can alleviate the pseudo-touching. It achieves an average P-FM of 97.73 which is two percentage points higher than the result of U-Net. The proposed approach can also accept common challenges including non-uniform illumination, stains, noise and delivers finer performance across several metrics.
P Zhao, W Wang, Z Cai, G Zhang, Y Lu
IEEE Access
2021y Nov
Accurate layout analysis without subsequent text-line segmentation remains an ongoing challenge, especially when facing the Kangyur, a kind of historical Tibetan document featuring considerable touching components and mottled background. Aiming at identifying different regions in document images, layout analysis is indispensable for subsequent procedures such as character recognition. However, there was only a little research being carried out to perform line-level layout analysis which failed to deal with the Kangyur. To obtain the optimal results, a fine-grained sub-line level layout analysis approach is presented. Firstly, we introduced an accelerated method to build the dataset which is dynamic and reliable. Secondly, enhancement had been made to the SOLOv2 according to the characteristics of the Kangyur. Then, we fed the enhanced SOLOv2 with the prepared annotation file during the training phase. Once the network is trained, instances of the text line, sentence, and titles can be segmented and identified during the inference stage. The experimental results show that the proposed method delivers a decent 72.7% average precision on our dataset. In general, this preliminary research provides insights into the fine-grained sub-line level layout analysis and testifies the SOLOv2-based approaches. We also believe that the proposed methods can be adopted on other language documents with various layouts.





